Introduction to Detectable Materials, Products, and Inspection Approaches
Why do we need metal detectable materials?
In the food production and packaging industry, the primary goal is to manufacture and deliver high-quality, healthy, and safe products for consumers. To achieve this goal requires the implementation of strict quality control methods to prevent food contamination. One of the most common sources of food contamination are from broken or worn equipment component; especially during production and packaging operations.
Broken or dilapidated equipment has the risk of being highly mixed with larger assembly equipment and small volume materials. If the “foreign body contamination” are not found or managed, it will reduce the quality of food and bring health and safety risks to consumers. Many industry professionals use metal and plastic tools and equipment to prevent these problems from occurring. Compared with other physical contaminants, plastic and rubber contaminants are difficult to reflect conductive, magnetic, or high-density characteristics through metal detection or X-ray detection systems under normal conditions. However, they play a most common and important roles in machinery and food processing, so they have an increased risk of becoming foreign objects. This is where the use of detectable plastic materials becomes more important, especially when food manufacturers have regulatory and ethical obligations, they should do their responsibilities and take clear measures to minimize the risk of foreign objects.
In addition, owners of famous brand, retailers and restaurant chains insist that food processors use metal and X-ray detectable plastic and rubber products. This has become part of the HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) program of many companies.

Recently, the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) requires agricultural manufacturers, food processors, and packagers to implement hazard analysis and risk-based prevention and control (HARPC) to prevent physical damage such as glass, metal, wood, plastic, and other contaminants enter the market. The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) considers contaminants longer than 0.275 inches (7mm) to be dangerous. Growers, packers, and food processors are using their existing metal detectors and x-ray inspection systems with plastic detectable to prevent plastic-contaminated food from handing over to consumers.
What are metal detectable materials and what are the related applications?
As the name implies, metal detectable plastics have optical and metal detection characteristics, standard components with metal powder, made of techno polymers, all resins, including thermoplastics and thermosetting resins, can add additives to make metals at an affordable price and be detectable. These additives make the material enough sensitive to magnetism, so it is conductive, and can use standard metal detectors or X-ray machines to detect unwanted particles. Additives allow the detection of very small particles as small as 27mm. Plastics such as polyethylene (UHMW), polypropylene, polycarbonate, PEEK, nylon (PA6), and acetal can be treated with these additives. The color of detectable plastics is usually blue, which is achieved using gray additives. However, PE-UHMW is dark gray. PEEK metal detectable materials are used in applications where high line speeds require high wear resistance or operating temperatures above 130°C (266°F). Not all metal detectable plastics are allowed to pass X-ray inspection. Acetal and PA6 are fine, but PEEK cannot. Metal detectable the blue color of acetal and nylon allows visual inspection. Generally, plastics have impact resistance, so in processing and packaging machinery and tools, high-stress plastic parts are less damaged.
Metal detectable plastics are mainly used in components and products in the food production and packaging industry. They allow professionals to use metal detectors to reduce the risk of food damage or plastic contamination caused by worn-out tools and equipment. In addition, compared to metal components, they help reduce item weight and/or noise emissions.
For example,- Components of food processing equipment, such as mixing paddles
- Parts of material processing equipment, such as material hoppers
- Food measuring tools, such as measuring cups
- Food operating products, such as knives, shovels, scrapers, molds
- Food packaging and storage devices, such as trays
Types of metal detectable products and materials
The detectable products and materials can be divided into four main types:
1. Metal Detectable2. Part Metal Detectable
3. X-ray Visible
4. Dual Detectable
Metal Detectable products
In the late 1980s, the first batch of detectable products were used in food production, which was characterized by embedding or sticking iron filings into items with high risk of contamination, so that if they were mistakenly entered, they would trigger a metal detector at the end of the production line.
Products manufactured in this way are the most common approach for plastic and rubber products. The ferromagnetic content in the material triggers the warning reaction of the metal detector in the same way as the standard metal contaminants. However, because the detectable material only contains a small part of the metal content, current technology in most food production environments, metal detectors can reliably detect detectable plastic and rubber fragments about the size of a 10 mm diameter sphere, but they need to be properly calibrated. In contrast, the diameter of pure iron contaminants is about 1mmØ. In certain environments such as nutraceutical manufacturing, a small metal detector aperture can achieve a very high level of iron detection sensitivity, which means that it can reliably detect fragments of 0.6 mm wide detectable plastic bristles.
Part Metal Detectable Products
It is not always possible or practical to make the entire composition of an item metal detectable. Examples include woven polypropylene mesh hair and beard nets which contain steel clasps to provide metal detectable properties. By being part metal detectable the foreign body contamination risk is significantly decreased, however food manufacturers should be conscious of the fact that if the item is fragmented through a process such as cutting, blending, or mixing, then nondetectable fragments will remain. This should be recorded as part of risk assessment.
X-Ray Visible Products
X-ray inspection works completely different from metal inspection. Therefore, a common mistake is to misunderstand that metal detectable products are also X-ray detectable. Ferromagnetic additives are used to make plastic or rubber detectable to achieve metal detectability, however, food-safe ultra-high-density additives (with high atomic number) must be used to achieve good X-ray contrast performance. When these additives are added to the polymer in the correct proportion, the X-ray inspection system can detect fragments as small as 3mmØ, and can use the "specific gravity" to compare the density of the material. The specific gravity is the mass of the substance in the same given volume and the mass of the reference substance. Ratio. The specific gravity is expressed in grams per cubic centimeter. For example, the specific gravity of water is 1.00g/cm³, which is usually used as a fixed point for comparison. Any solid material with SG less than 1.0 will float in the water, and anything 1.0+ will sink. The specific gravity of polypropylene is 0.95g/cm³, wood is about 0.60g/cm³, and steel is 7.50g/cm³. Although ferromagnetic additives do increase the specific gravity of the base polymer, they are not always sufficient to achieve reliable X-ray detectability, and not all manufacturers of detectable products can correctly distinguish between metal detectable materials and X-ray detectable Materials, which further aggravated the chaos of the entire industry.
Dual Detectable Products
In 2009, some companies have developed a plastic compound containing appropriate levels of ferromagnetic and high-density additives that can trigger metal detection and X-ray detection systems at the same time, while still functioning as a high-performance polymer.
A Guide to Metal Detectable Inspection. How does it work?
The most used metal detection systems that are in use by food manufacturers operate on a principle known as the “balanced coil” system. They operate by using three equidistant coils that surround the opening (aperture) through which the product under test passes. The center coil is connected to an oscillator circuit that generates a magnetic field. The two equally spaced receiving coils on either side of the center coil receive an equal amount of this signal.
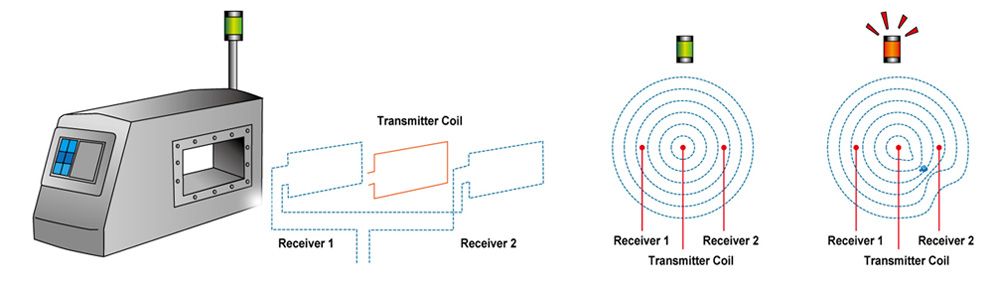
Since the coils are wound in opposite ways to each other, the net signal on the receiver coil is zero. When contaminants pass through the aperture, it will change the balance of the coil, and the final signal will no longer be zero; therefore, if the contaminants change the balance between the receivers, it will trigger a non-passing reaction; the weakest part of the metal detector is the geometric center of the aperture is also the most difficult place to detect. If possible, the contaminants should be tested here when testing and calibrating the detector.
Metal detectors can detect three main types of metal contaminants: ferrous, non-ferrous, and stainless steel. Among them, ferrous contaminants are the easiest to detect because they are conductive and magnetic; Non-ferrous contaminants are not magnetic, but they have good conductivity; the most difficult to detect are stainless steel contaminants, because they are often non-magnetic and the conductivity is poor, which means that the metal detector can detect ferrous materials smaller than stainless steel.
When discussing sensitivity, this refers to the smallest piece of contaminant that the detector can detect when a specific product is set to pass, and it is usually tested using a calibration specimen containing contaminant spheres measured in millimeters. Therefore, you may use a ferrous test piece which contains a 3mm size of contaminant sphere.
The following is the inspection for metal detectable zip ties:
- First, Cut 3mm piece from the head, body, and tail of a cable tie as test samples.
- Second, put one piece of sample on a Styrofoam with a thickness of 25mm and pass it through the metal detector.
- Third, the cable tie is deemed to pass the test if the samples from its head, body and tail are all detected by the metal detector.
In addition to the above-mentioned testing methods, Hua Wei has also enhanced the difficulty of metal detection testing. To make sure the function of metal detection, the test has been through thorough, rigorous and repeated in-plant validation, as well as industry and partner customer validation, and all the test results can be proven the performance is superior to other brands. The following is a description of the more stringent testing method.
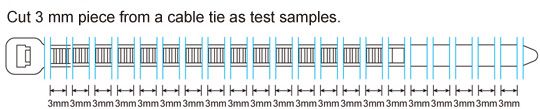
- Cut a cable tie into pieces every 3mm. For example, a 200mm long metal detectable cable tie can be cut into approximately 62~64 pieces, and each piece needs to pass through the metal detector and can be detected (the picture below for reference).
- The sensitivity setting of the metal detector is set to "general standard" and "the least sensitive parameter", in which case each fragment of all the cable tie must be detectable by the metal detector.
Hua Wei is your best option of suppliers!
Over the years, since engineering plastics can increase the speed and/or the lifespan of products, food production and packaging industries have increasingly accepted engineering plastics as a substitute for metal. This positive trend has led to an increase in demand for plastics, leading to the development of better and safer plastics. Metal detectable products can transform the industry from metal parts to plastic parts without worrying about whether the material fragments will fall off and mix with food.
To learn more about metal detection of plastics or our series of products , please contact us.
New Product
Featured product
 Hot
Hot
Stainless Steel Ties
 Hot
Hot
Stainless Steel Ties
With high resistance to various corrosive agents such as acids, alkali, UV, and rust, …
Read More Hot
Hot
Wire Ducts
 Hot
Hot
Wire Ducts
The premium solution for routing and hiding wires in control panels.
Read More Hot
Hot
Standard Cable Ties
 Hot
Hot
Standard Cable Ties
Available materials include heat stabilized, weather resistant and flame retardant polymers,...
Read More Hot
Hot
(GIT-703) Cable Tie Tensioning Tool
 Hot
Hot
(GIT-703) Cable Tie Tensioning Tool
The new cable tie installation tool can fasten and cut nylon cable ties quickly & safely
Read More



